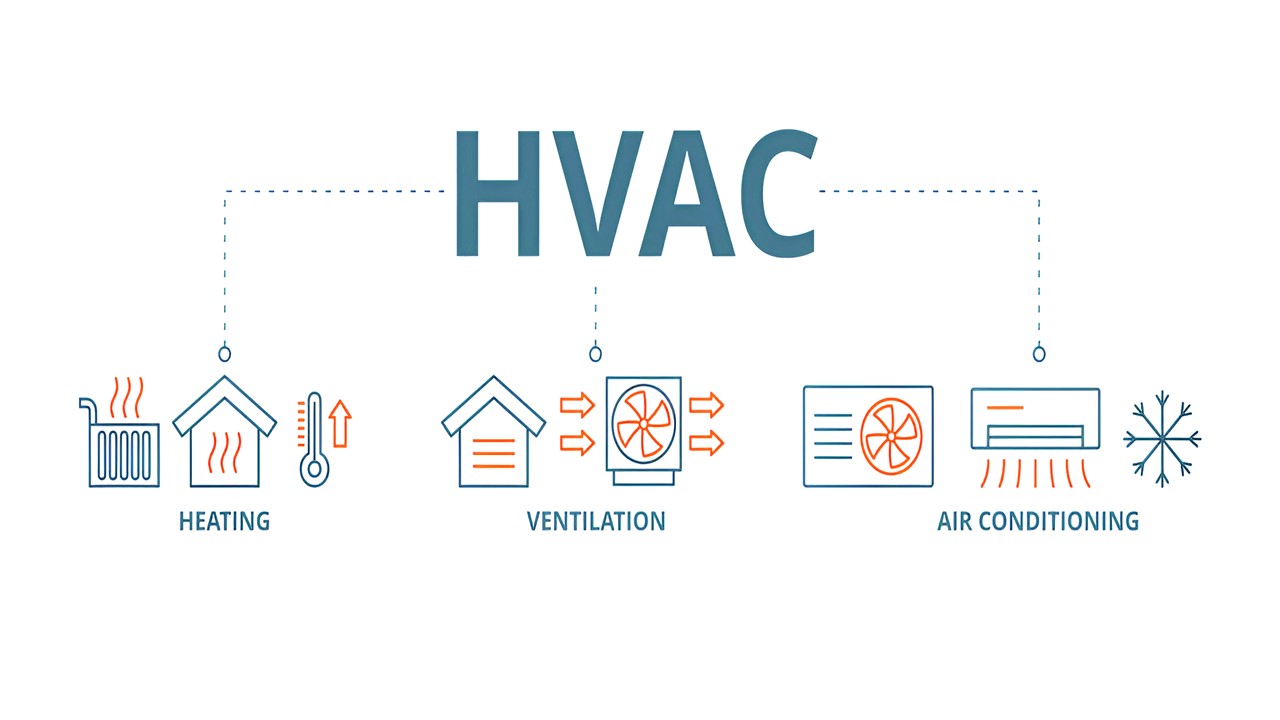
Modern HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system design requires a sophisticated understanding of various heat transfer mechanisms. Among these, thermal radiation plays a pivotal yet often underappreciated role in determining system efficiency and occupant comfort. This comprehensive analysis explores the fundamental principles of thermal radiation in HVAC systems and examines cutting-edge approaches to leveraging its benefits.
1. Understanding Thermal Radiation: Core Principles
Thermal radiation represents a unique heat transfer mechanism that occurs through electromagnetic waves emitted by all objects with temperatures above absolute zero. Unlike conduction and convection, which require a physical medium for heat transfer, thermal radiation can propagate through a vacuum. This distinctive property makes it a crucial consideration in indoor environmental design, as it directly influences how heat interacts with building surfaces and occupants.
2. Critical Impact on HVAC System Performance
2.1. Heat Transfer Dynamics
Thermal radiation significantly contributes to the overall heat transfer within indoor spaces through multiple pathways:
-
- Direct solar radiation through windows and building envelope
- Heat exchange between interior surfaces at different temperatures
- Radiative heat transfer between occupants and their surroundings
- Interaction with building materials and thermal mass
2.2. Solar Heat Gain Management
One of the most significant challenges in HVAC design is managing solar heat gain effectively. This involves:
-
- Strategic window placement and orientation
- Implementation of advanced shading solutions
- Selection of appropriate glazing materials and coatings
- Integration of automated shading systems that respond to solar conditions
2.3. Occupant Comfort Optimization
The perception of thermal comfort is heavily influenced by radiative heat exchange. Key considerations include:
-
- Surface temperature management to maintain optimal radiant temperatures
- Balance between air temperature and mean radiant temperature
- Uniform temperature distribution to prevent localized discomfort
- Consideration of activity levels and occupant positions within spaces
3. Innovative Technologies and Design Approaches

3.1. Advanced Radiant Systems
Modern HVAC design increasingly incorporates sophisticated radiant heating and cooling solutions:
-
- Hydronic systems embedded in floors, walls, or ceilings
- Integration with thermal mass for improved energy storage
- Hybrid systems combining radiant and conventional approaches
- High-efficiency panels for targeted heating or cooling
3.2. Thermal Mass Utilization
Strategic use of thermal mass enhances system performance through:
-
- Heat absorption during peak periods
- Delayed release of stored thermal energy
- Temperature stabilization across daily cycles
- Reduced peak loads on mechanical systems
3.3. Smart Control Integration
Contemporary HVAC systems leverage advanced control strategies:
-
- Real-time monitoring of radiant heat contributions
- Dynamic adjustment of system parameters based on environmental conditions
- Predictive control algorithms for optimal energy management
- Integration with building automation systems
3.4. Simulation and Modeling
Modern design tools enable sophisticated analysis of thermal radiation:
-
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling of heat transfer
- Detailed simulation of surface temperature distributions
- Integration of multiple heat transfer mechanisms
- Optimization of system design before implementation
4. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Benefits
4.1. Reduced Energy Consumption
Proper consideration of thermal radiation can lead to significant energy savings:
-
- 30-40% reduction in energy use compared to conventional systems
- Decreased reliance on mechanical cooling
- Optimized operation during partial load conditions
- Enhanced natural heat transfer utilization
4.2. Environmental Impact
The implementation of radiation-aware HVAC design contributes to sustainability through:
-
- Lower carbon emissions from reduced energy consumption
- Decreased reliance on refrigerants
- Extended equipment life due to optimized operation
- Improved indoor air quality through reduced air movement
5. Technical Challenges and Solutions
5.1. Design Complexities
Several challenges must be addressed in radiation-aware HVAC design:
-
- Complex interactions between different heat transfer mechanisms
- Accurate modeling of radiative heat exchange
- Integration with existing building systems
- Material selection for optimal performance
5.2. Implementation Strategies
Successful implementation requires careful consideration of:
-
- System sizing and capacity calculations
- Control system design and optimization
- Installation methods and quality control
- Commissioning and performance verification
6. Future Directions and Emerging Technologies
The field continues to evolve with new developments in:
- Advanced materials with enhanced radiative properties
- Improved simulation and modeling capabilities
- Integration with renewable energy systems
- Smart building technologies and automation
7. Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing thermal radiation is crucial for creating high-performance HVAC systems. By incorporating advanced technologies, smart controls, and innovative design approaches, engineers can develop solutions that optimize energy efficiency while maintaining superior indoor environmental quality. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of thermal radiation in HVAC design will become increasingly important for achieving sustainable and comfortable indoor environments.
8. References
- https://www.ijser.org/researchpaper/Energy-Efficient-HVAC-System-Designing-and-Simulation-of-Radiant-Cooling-System.pdf
- https://www.thermalcontrolmagazine.com/cover-story/comfort-meets-efficiency/
- https://www.mdpi.com/journal/energies/special_issues/43Y3RI3A5B
- https://www.mgsarchitecture.in/building-materials-products/technology-automation/1252-radiant-cooling.html
- https://www.simscale.com/blog/radiation-and-thermal-comfort/
- https://www.kingsresearch.com/blog/hvac-insulation-maintaining-comfortable-indoor-temperatures
- https://blog.goodwindco.in/radiation-thermal/
- https://www.simscale.com/blog/radiation-heat-transfer-release/
- https://www.heinenhopman.com/how-does-thermal-radiation-affect-hvac-systems/
- https://blog.goodwindco.in/thermal-radiation/
- https://www.heinenhopman.com/how-does-thermal-radiation-affect-hvac-systems/
- https://blog.goodwindco.in/radiation-thermal/
- https://nzeb.in/knowledge-centre/hvac-2/radiant-cooling-systems/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radiant_heating_and_cooling