1. Introduction
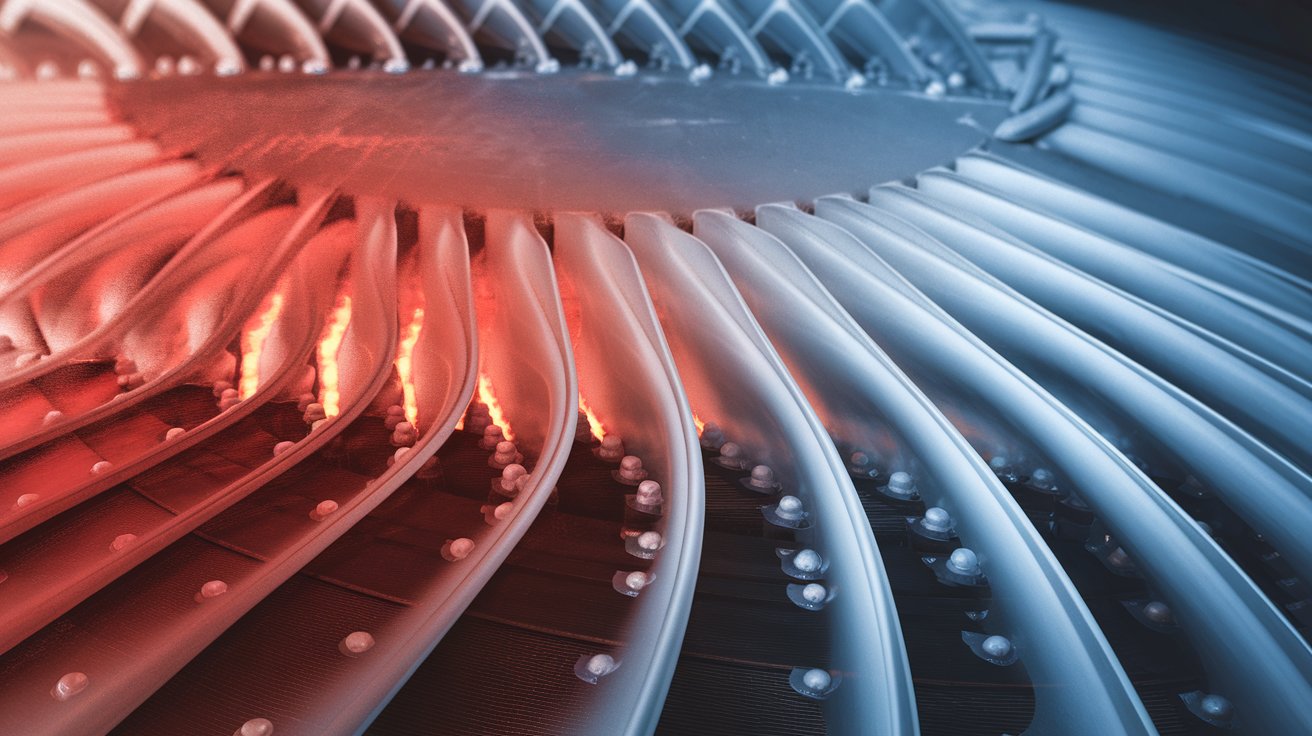
Gas turbine blades operate in extraordinarily harsh environments, facing temperatures that exceed their materials’ melting points while enduring extreme pressures and mechanical stresses. Effective cooling solutions are not just beneficial but essential for their performance, longevity, and efficiency. Without proper cooling, these critical components would rapidly fail due to creep, oxidation, and thermal fatigue.
 2. Critical Role of Cooling in Gas Turbines
2. Critical Role of Cooling in Gas Turbines
Cooling gas turbine blades serves multiple crucial functions:
-
- Prevents structural damage and extends component lifespan
- Improves overall fuel efficiency
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Enables operation at higher temperatures for improved performance
- Maintains blade integrity under extreme conditions
3. Advanced Cooling Techniques
3.1. Film Cooling
One of the most effective methods for protecting turbine blades from high-temperature gases, film cooling creates a protective barrier between the blade surface and hot gases. This technique involves ejecting a thin layer of coolant (typically air) over the blade surface. The effectiveness of film cooling has been enhanced through:
-
- Optimized geometry and arrangement of cooling holes
- Improved distribution patterns for maximum coverage
- Enhanced heat transfer efficiency
- Reduced thermal stress on blade materials
3.2. Internal Cooling Channels
Modern turbine blades incorporate sophisticated internal passages that allow coolant circulation within the blade structure. Key developments include:
-
- Integration of rib turbulators to enhance heat transfer
- Complex channel geometries for improved coolant flow
- Strategic placement of cooling passages in critical areas
- Enhanced turbulence promotion for better heat dissipation
3.3. Effusion Cooling
This method employs a network of small holes distributed across the blade surface to inject coolant directly into the hot gas path. Recent advances include:
-
- Creation of complex porous structures through additive manufacturing
- Improved coolant distribution patterns
- Enhanced mechanical strength while maintaining cooling effectiveness
- Optimized hole patterns for maximum cooling efficiency
3.4. Transpiration Cooling
An advanced technique utilizing porous materials that allow coolant to permeate through the blade surface. Features include:
-
- Uniform cooling across the entire blade surface
- Adaptability to varying operational conditions
- Customizable coolant flow rates
- Minimized thermal gradients across the blade
3.5. Impingement Cooling
Particularly effective for high-heat areas like the leading edge, this technique involves directing coolant jets onto specific blade regions. Advancements include:
-
- Optimized jet patterns through CFD simulations
- Enhanced heat transfer rates in critical areas
- Improved targeting of high-thermal-load regions
- Integration with other cooling methods for maximum effectiveness
4. Advanced Materials and Technologies
4.1. Material Innovations
4.1.1. Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs)
-
- Superior temperature resistance compared to traditional alloys
- Reduced cooling requirements
- Enhanced structural integrity
- Improved overall performance
4.1.2. Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs)
-
- Advanced insulation against extreme heat
- Protection of underlying blade materials
- Extended component lifespan
- Improved thermal management
4.2. Technological Advances
4.2.1. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
-
- Advanced simulations for cooling design optimization
- Pre-prototype performance evaluation
- Analysis of various operating conditions
- Enhanced design efficiency
4.2.2. Additive Manufacturing
-
- Creation of complex cooling channel geometries
- Implementation of sophisticated internal structures
- Improved heat dissipation capabilities
- Manufacturing of previously impossible designs
4.2.3. Digital Twin Technology
-
- Real-time performance simulation
- Predictive maintenance capabilities
- Optimization of cooling strategies
- Continuous monitoring of temperature distributions
5. Layered Cooling Technologies
Modern turbine designs often integrate multiple cooling methods to create comprehensive thermal management systems. This approach combines:
- Film cooling for surface protection
- Internal convection for core temperature control
- Impingement cooling for targeted thermal management
- Transpiration cooling for uniform temperature distribution
6. Real-World Applications
6.1. Aerospace Industry
-
- Enhanced jet engine performance
- Improved reliability and durability
- Extended component life
- Higher operating temperatures
- Reduced maintenance requirements
6.2. Power Generation
-
- Improved plant efficiency
- Reduced emissions
- Enhanced reliability
- Continuous operation capability
- Better thermal management
6.3. Renewable Energy
-
- Advanced wind turbine cooling
- Adaptation to environmental conditions
- Improved energy production consistency
- Enhanced component durability
7. Challenges and Considerations
7.1. Current Challenges
-
- High equipment and implementation costs
- Complex design and manufacturing requirements
- Material compatibility issues
- Maintenance of cooling effectiveness
- Integration with existing systems
7.2. Design Considerations
-
- Balancing cooling effectiveness with aerodynamic efficiency
- Managing coolant flow requirements
- Optimizing material selection
- Ensuring system reliability
- Maintaining cost-effectiveness
8. Future Directions
- Development of hybrid cooling systems
- Integration with renewable energy sources
- Advanced control algorithms
- Improved energy efficiency
- Enhanced material compatibility
- Cost reduction strategies
9. Conclusion
The evolution of gas turbine blade cooling technologies represents a critical advancement in thermal management engineering. Through the integration of sophisticated cooling techniques, advanced materials, and cutting-edge manufacturing processes, these innovations enable higher operating temperatures while maintaining structural integrity. As research continues and technology advances, we can expect further improvements in turbine design that will push operational limits while maintaining reliability and efficiency. The continued development of these cooling solutions remains crucial for meeting future energy demands while minimizing the environmental impact
10. References
- [Review of Advanced Effusive Cooling for Gas Turbine Blades](https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/22/8568)
- [Efficient Gas Turbine Blade Cooling Simulations](https://prismecs.com/blog/efficient-gas-turbine-blade-cooling-simulations)
- [An Insight into Gas Turbine Blades: Materials, Design, and Applications](https://karkhana.io/an-insight-into-gas-turbine-blades-materials-design-and-applications/)
- [Advances in Gas Turbine Blade Cooling Technology](https://www.witpress.com/Secure/elibrary/papers/HT08/HT08014FU1.pdf)
- [Development Trend of Cooling Technology for Turbine Blades](https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/16/2/668)
- https://karkhana.io/an-insight-into-gas-turbine-blades-materials-design-and-applications/
- https://www.witpress.com/Secure/elibrary/papers/HT08/HT08014FU1.pdf
- https://www.ripublication.com/ijaerspl2018/ijaerv13n5spl_10.pdf
- https://www.mdpi.com/2411-5134/8/1/21
- https://www.ijert.org/research/external-and-internal-cooling-techniques-in-a-gas-turbine-blade-an-overview-IJERTV10IS080055.pdf
- NETL (2024). “Enhanced Internal Cooling of Turbine Blades.” [PDF](https://netl.doe.gov/sites/default/files/gas-turbine-handbook/4-2-2-2.pdf)
- Penn State University (2024). “Innovating Turbine Cooling.” [Link](https://sites.psu.edu/turbine/project/innovating-turbine-cooling/)
- Scrap Gators (2024). “Innovative Advancements in Gas Turbine Solutions.” [Link](https://www.scrapgators.com/innovative-advancements-in-gas-turbine-solutions)
Note: The blog is created by referring above links and is thoroughly verified by content team. We prioritize accuracy and quality in every article.